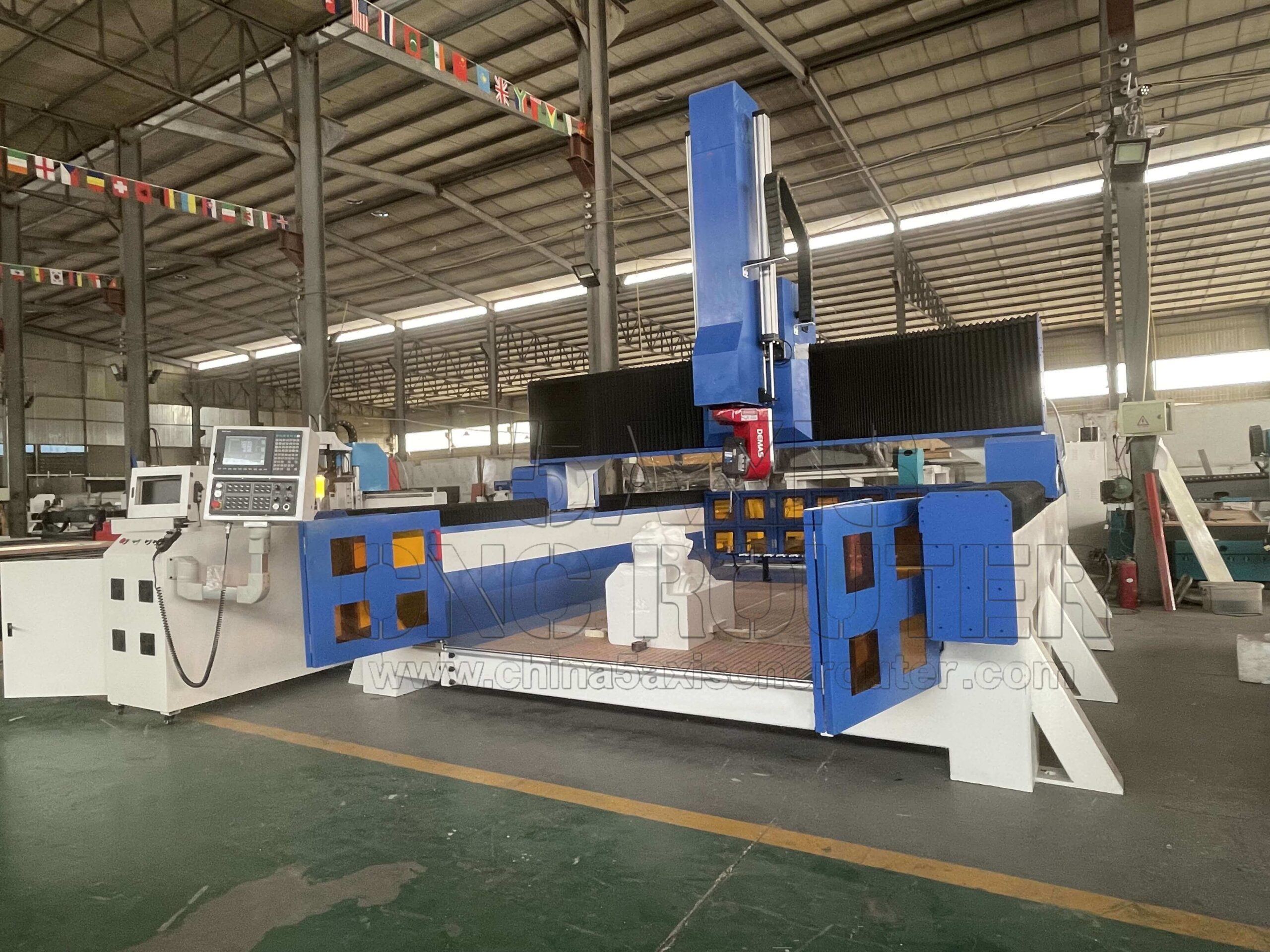
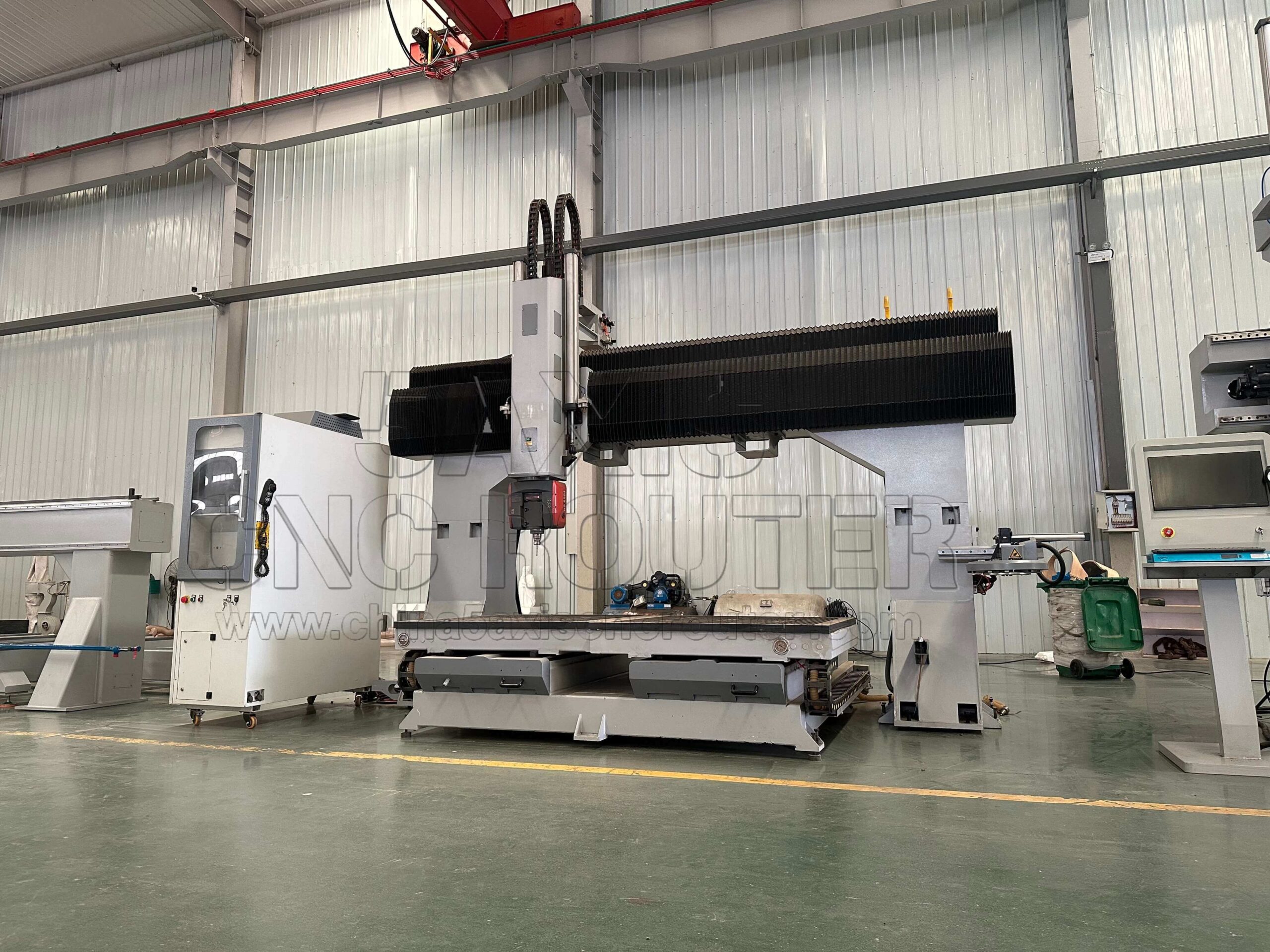
What Is a 5 Axis CNC Router and How Does It Work?
Compared with conventional 3-axis CNC routers, a 5 axis machine allows the cutting tool or the workpiece to move along five different axes simultaneously, enabling multi-directional machining in a single setup.
In modern manufacturing, this capability is especially valuable for applications involving complex curved surfaces, deep cavities, undercut features, and free-form geometries. As product designs become more complex and tolerance requirements tighter, understanding how a 5 axis CNC router works—and when it is truly necessary—has become an important part of equipment selection for industrial manufacturers.
This article explains the technical fundamentals of 5 axis CNC routing, compares it with other CNC configurations, and outlines its practical advantages and limitations from an engineering perspective.
Table of Contents
What Is a 5 Axis CNC Router?
A 5 axis CNC router is a numerical control machine that combines three linear motion axes with two rotational axes. The three linear axes—X, Y, and Z—control movement in horizontal and vertical directions. The additional two axes allow the tool or the workpiece to rotate, enabling the cutting tool to approach the material from multiple angles.
This multi-axis capability allows complex parts to be machined without repeatedly repositioning the workpiece. Instead of stopping the machine, manually re-clamping the part, and recalibrating reference points, a 5 axis CNC router performs continuous machining while dynamically adjusting tool orientation.
Industrial 5 axis CNC routers are typically designed with rigid mechanical structures, high-precision linear motion systems, and advanced CNC controllers to support stable, simultaneous multi-axis operation over long production cycles.
How Does a 5 Axis CNC Router Work?
The Five Axes Explained
A standard 5 axis CNC router operates using the following axes:
- X Axis: Linear movement left and right
- Y Axis: Linear movement forward and backward
- Z Axis: Vertical movement up and down
- A Axis: Rotation around the X axis
- B or C Axis: Rotation around the Y or Z axis, depending on machine design
The rotational axes allow the cutting tool to tilt and rotate relative to the workpiece surface. This makes it possible to maintain optimal cutting angles even on complex geometries.
Simultaneous Multi-Axis Machining
In true 5 axis machining, all five axes move simultaneously during cutting. This is known as continuous or simultaneous 5 axis interpolation. The CNC controller continuously calculates coordinated movements across all axes to follow complex tool paths while maintaining stable cutting conditions.
Compared to indexed or positional machining—where rotational axes are fixed before cutting—simultaneous machining produces smoother surface finishes, reduces tool marks, and improves overall dimensional accuracy.
Role of CNC Control Systems and CAM Software
5 axis CNC routing relies heavily on advanced CAM software capable of generating multi-axis tool paths. These systems convert 3D CAD models into coordinated motion commands that account for tool orientation, collision avoidance, and material removal strategies.
The CNC controller executes these commands in real time, ensuring precise synchronization between linear and rotational movements throughout the machining process.
Differences Between 3 Axis, 3+2 Axis, and 5 Axis CNC Routing
3 Axis CNC Routing
A 3 axis CNC router allows movement along the X, Y, and Z axes only. The cutting tool always approaches the workpiece from a single vertical direction. While this configuration is sufficient for flat panels and simple geometries, complex parts require multiple setups and manual repositioning.
This increases production time and introduces cumulative alignment errors.
3+2 Axis CNC Routing
A 3+2 axis CNC router allows the workpiece or spindle to be positioned at fixed angles using two rotational axes before machining begins. Cutting still occurs along three linear axes at a time, but from different orientations.
This approach improves access to angled surfaces but does not allow continuous tool orientation during cutting. Surface continuity and efficiency are still limited compared to true 5 axis machining.
True 5 Axis CNC Routing
A true 5 axis CNC router enables continuous movement along all five axes during machining. This allows complex features, undercuts, and free-form surfaces to be machined in a single setup with consistent tool engagement.
From an engineering standpoint, this configuration offers the highest flexibility, accuracy, and efficiency for complex geometry machining.
Industrial Applications of 5 Axis CNC Routers
Mold Manufacturing
Mold components often feature complex cavities, smooth curved surfaces, and tight tolerance requirements. A 5 axis CNC router allows these features to be machined with fewer setups, improving surface quality and reducing lead times.
Aerospace and Prototyping
In aerospace and advanced prototyping applications, parts frequently require complex shapes and precise dimensional control. 5 axis CNC routers are commonly used for machining lightweight materials, tooling models, and composite components.
Composite and Plastic Processing
Composite materials benefit from controlled cutting angles to reduce delamination and edge damage. Multi-axis machining ensures optimal tool orientation and cleaner cut edges.
High-End Woodworking and Architectural Components
In architectural fabrication and custom woodworking, 5 axis CNC routers enable sculpted forms, curved structures, and complex decorative elements that are difficult to produce with conventional CNC systems.
Advantages of Using a 5 Axis CNC Router
From an engineering perspective, the main advantages include:
- Reduced number of setups and fixtures
- Improved dimensional accuracy
- Better surface finish on complex geometries
- Shorter machining cycles
- More consistent production results
- Improved tool life due to optimized cutting angles
These benefits are particularly significant in applications where geometric complexity directly impacts product performance or aesthetic quality.
Limitations and Boundary Conditions
Despite their advantages, 5 axis CNC routers are not suitable for every manufacturing scenario.
- They are generally optimized for wood, composites, plastics, and non-ferrous metals rather than heavy-duty steel machining.
- Programming and operation require more advanced technical knowledge.
- Initial investment and system complexity are higher than basic CNC routers.
For high-volume heavy metal cutting, a dedicated machining center may be more appropriate.
Understanding these limitations is essential to selecting the correct equipment for a given application.
When Do You Really Need a 5 Axis CNC Router?
A 5 axis CNC router becomes a practical necessity when production involves:
- Complex curved or free-form surfaces
- Undercut features inaccessible from a single direction
- High surface quality requirements without secondary finishing
- Reduced setup time and improved process consistency
If these requirements are central to your manufacturing process, a true 5 axis solution provides long-term efficiency and quality advantages.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a 5 axis CNC router?
A 5 axis CNC router is a machine that allows simultaneous movement along five axes, enabling complex 3D machining in a single setup.
How does a 5 axis CNC router improve surface quality?
By maintaining optimal tool orientation during cutting, it reduces tool marks and produces smoother surfaces.
Is 5 axis CNC routing difficult to operate?
Programming and operation are more complex than 3 axis systems, but modern CAM software and proper training significantly reduce the learning curve.
What materials can be machined with a 5 axis CNC router?
Typical materials include wood, plastics, composites, and aluminum, depending on machine configuration.
Are there applications where a 5 axis CNC router is not suitable?
Heavy-duty steel machining is usually better handled by machining centers rather than CNC routers.
Conclusion
A 5 axis CNC router is a powerful manufacturing tool for producing complex geometries with high precision and consistent quality. By enabling simultaneous multi-axis machining, it reduces setup time, improves accuracy, and expands design possibilities. Understanding both its capabilities and limitations allows manufacturers to make informed decisions when selecting advanced CNC equipment.
Products Categories
Recently News
Why Choose Us
1.Experienced CNC manufacturer.
2.Strong R&D and innovation.
3.High-quality machine components.
4.Custom solutions available.
5.Strict quality control.
6.Fast production and delivery.
7.Professional technical support.
8.Competitive factory pricing.
9.Trusted by global customers.
10.One-stop CNC solutions.
Contact Us
- Wechat: ExtraCNC
- Whatsapp/Moblie:0086 15562628072
- Email: [email protected]